
Every year, natural disasters such as hurricanes, tornadoes, and severe thunderstorms affect millions of people around the world. These disasters can also affect your infrastructure. And not only natural disasters are a danger, but also data loss, a cyber attack or downtime. This blog will show you how to easily create a disaster recovery solution for your cloud infrastructure.
What is the likelihood of a disaster occurring in your company? And how likely is it that the company will go bankrupt as a result of the disaster? These are two questions that will assist you in determining the importance of a disaster recovery solution for your company. A disaster recovery plan ensures that your company's most critical IT systems are operational again immediately following a disaster or incident.
What is a disaster recovery plan?
A disaster recovery plan outlines the procedures that must be followed in the event of a disaster, as well as which type of recovery is required at what time. The plan identifies all risks and offers solutions to them. A disaster recovery plan should include the following elements:
- Recovery Point Objective (RPO)
- Recovery Time Objective (RTO)
💡 A Disaster Recovery Plan is exclusively focused on data and infrastructure, unlike a Business Continuity Plan which concerns the entire organization.
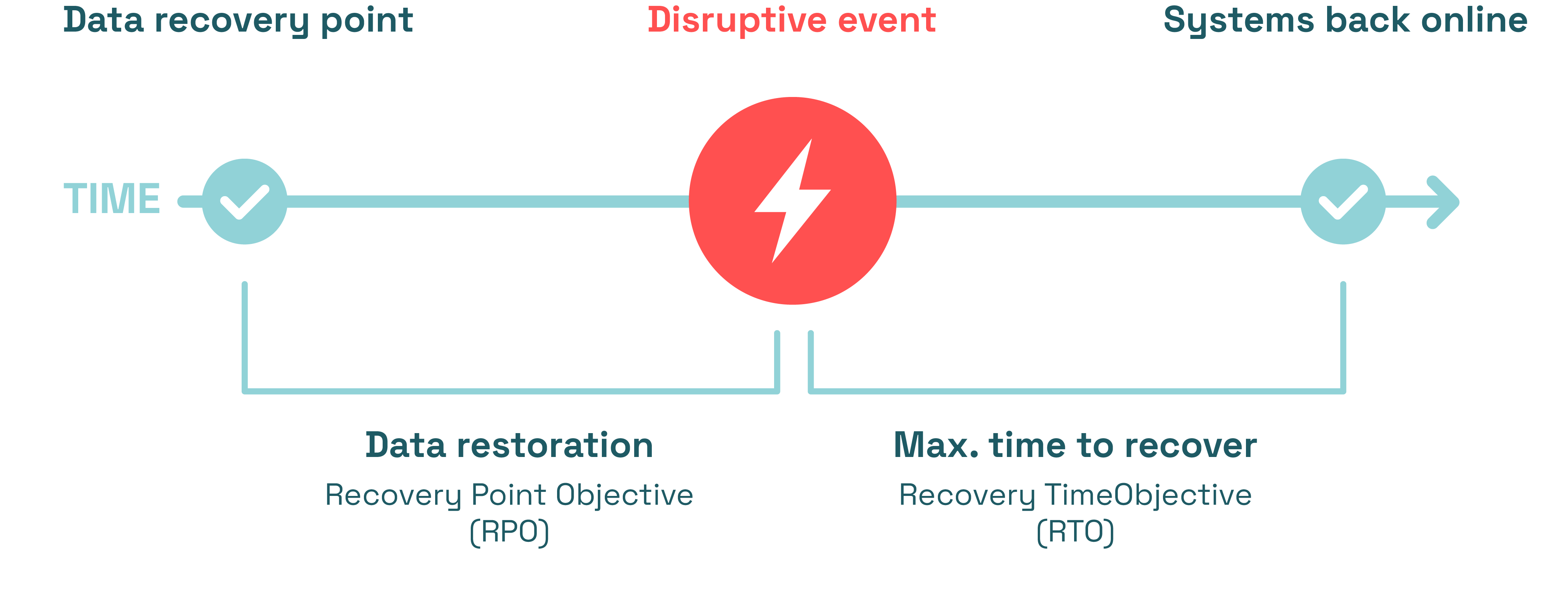
Recovery Point Objective (RPO) & Recovery Time Objective (RTO)
Recovery Point Objective (RPO) and Recovery Time Objective (RTO) are critical when developing a disaster recovery plan.
Recovery Point Objective
The Recovery Point Objective (RPO) specifies the maximum amount of data that can be lost and the frequency with which it must be restored. Is your maximum loss, for example, 6 hours? Then you must perform a backup every 6 hours.
Recovery Time Objective
The Recovery Time Objective (RTO) specifies the maximum amount of time it may take before you are operational again. It is critical to estimate this in a realistic manner. A database, for example, can be quickly restored, whereas an interface can take longer. You save time by focusing on redundancy, clustering, and backups. Apart from the possibilities, it is also important to take privacy and costs into account.
How to determine the best RPO and RTO
Determining the right RPO and RTO is, of course, dependent on your organization. However, the steps outlined below will point you in the right direction:
- Determine how business-critical all of your infrastructure's components and applications are
- Determine how much data and time each component and application can and must lose
- Choose a solution that meets the required RPO and RTO
Disaster recovery solutions
What exactly is a disaster recovery solution, and what options are available? And which solution is best suited to your business or organization? Below is a short overview of some suitable options and strategies to minimise the RTO and RPO.
- No plan
It is (often) not the best plan, but some companies do not opt for a disaster recovery solution. Because they label themselves as 'too small', there is too much work involved or there is a price tag. This option is almost never recommended since risks have not been mapped out and therefore cannot be overseen. - Backup
Do you know how much time you can lose? Then you can back up your server every so many hours using backups. The last backup is the basis of your restore in case of incidents and disasters.
💡 Tip: An extra to the regular backup is the snapshot. With a snapshot you take an image of your entire server at a certain moment. With this you can restore your previous configuration in half an hour. - Managed backup
Do you want to be sure that all data is stored securely 24/7? Then you can also opt for managed backup. Your cloud provider, in this case, Tilaa, will then make backups of your Cloud VPS every 4 hours. Daily, weekly and monthly backups are saved. All data for the entire month is securely stored on another server in one of our other data centers and of course, we ensure a quick restore of the backup as soon as required. - A standby service standby (backup with hot site)
If you have a backup service, you can fall back on it in case of incidents or disasters. It is important that you host the second service on an extra Cloud VPS. Should it run on the same host, they would be affected at the same time. - Redundancy
You can also choose to duplicate the entire infrastructure and store it in 2 different data centers. For some businesses, this is also a legal requirement (for example for companies in the healthcare sector). The different data centers must be at least 40 kilometers apart for them to work. Both locations must also be completely separate in terms of network connections and power supply. - Replication
For some, data loss or downtime is not an option. Think of government institutions or banks. They often opt for replication: a real-time one-to-one copy is stored in the cloud and is ready to jump in at any time.
Tilaa: the preferred cloud partner
In this article, you've read everything about the disaster recovery plan. Tilaa is an expert in the field of business cloud computing. We offer our own public cloud and are experts on areas such as security and privacy. We assist organizations in building the cloud environment that is best suited to their needs.
Do you want to know which cloud solution suits you best or have any further questions? Feel free to contact us or use our configurator to get a customized setup!


